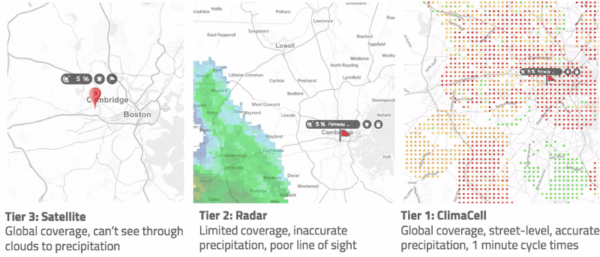
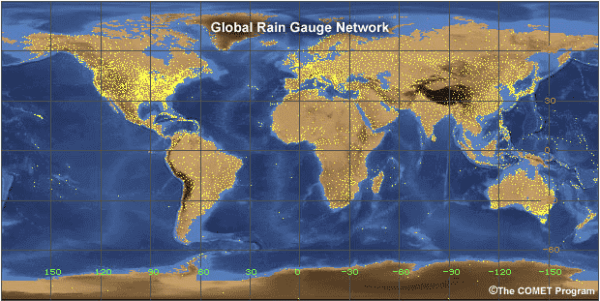
TL;DR:
- Energy demand is rising globally, driven by economic growth and population increase.
- Climate change poses challenges to renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower.
- Governments are passing legislation to transition to clean energy sources.
- Extreme weather events impact renewable energy generation and storage.
- Weather intelligence solutions like Tomorrow.io help renewable energy companies optimize operations and mitigate weather-related risks
The Rise of Energy Demand
Energy demand is soaring across the globe.
Studies project that the demand for energy will more than double by 2050, driven by economic growth and the rising population.
Today, only 14% of the world’s primary energy is sourced from renewable technologies. In the U.S., we are lucky to get up to 29% of our power from renewable sources.
However, we are still heavily reliant on fossil fuels.
Greenhouse gas emissions: the burning of coal, natural gas, and oil for electricity and heat is the largest single source of global GHG emissions.
The increasing energy demand results from several factors. As developing countries continue to industrialize and expand their economies, the need for reliable and accessible energy sources grows.
Additionally, the global population is expected to reach nearly 10 billion by 2050, further driving up the demand for energy to power homes, businesses, and transportation. This surge in energy consumption, if not addressed, will have significant implications for the environment and the fight against climate change.
Climate Crisis: Our Increasingly Volatile Weather
As a result of this need for energy, we are seeing climate policy flourish.
Energy demand is driving up the burning of fossil fuels for energy production, which is a major contributor to the climate crisis.
This has led hundreds of governments around the world to declare a climate emergency. These governments have committed to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050, or even earlier, in an effort to keep the global temperature increase to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels.
However, climate change already presents increasing challenges:
- More frequent and severe extreme weather events
- Changing precipitation patterns
- A progressive increase in temperature
Weather directly affects renewable resources like wind, solar, and hydroelectric power, which are crucial for the reliability and performance of the energy system.
Deliang Chen, professor of physical meteorology at the University of Gothenburg, notes:
“Their capacity is highly dependent on weather conditions, which makes their share in the existing energy system something of a challenge when it comes to reliability and stability.”
The Value of Renewable Energy to the World
Renewable energy can help combat rising global temperatures.
Under the most ambitious mitigation scenarios, renewable energy sources are projected to provide more than 60% of global electricity by 2050. Replacing fossil fuels with renewable energy sources, such as wind or solar farms, would dramatically reduce carbon emissions.
Plus, with advancements in technology, renewable energy is often becoming cheaper than traditional fossil fuel-based energy.
The good news is that the shift towards renewable energy is already underway!
Aside from our efforts to generate more renewables, many governments have passed legislation putting their cities on a path to clean energy:
- Minnesota: In February 2023, Minnesota passed a law that puts the state on a path to 100% clean electricity by 2040.
- California: In 2018, California passed Senate Bill 100, which requires the state to reach 100% renewable and zero-carbon electricity by 2045.
- New York: In 2019, New York passed legislation mandating 100% carbon-free electricity by 2040 and requiring 85% reductions in greenhouse gas emissions below 1990 levels by 2050.
- Washington: In 2019, Washington state passed the Clean Energy Transformation Act, which requires utilities to eliminate coal-fired electricity by 2025 and reach 100% carbon-neutral electricity by 2030.
- Hawaii: In 2015, Hawaii passed a law requiring the state to generate 100% of its electricity from renewable sources by 2045
While the transition to renewable energy has its challenges, the benefits make it a crucial step in securing a sustainable energy future for the world.
Some of the key benefits of renewable energy include:
- Reduced carbon emissions and environmental impact
- Increased energy security and independence
- Job creation in the renewable energy sector
- Cost-competitiveness with traditional fossil fuels
- Improved public health outcomes by reducing air and water pollution
As we try to improve our efforts with renewable energy, we need to understand the limitations of our current energy sources and think of ways to optimize their generation.
Earth’s Renewable Energy Sources
Solar Power
Severe weather events present increasing challenges for the generation and storage of solar energy.
High-impact storms can significantly damage solar panels and disrupt the supply of renewable energy, which is an ongoing challenge for the industry.
Just last year, the state of Nebraska saw one of their solar farms destroyed in minutes by severe hail storms in June 2023.
Solar farm in Nebraska destroyed by baseball-sized hail 🤯 https://t.co/S6x8zhK45Z pic.twitter.com/U7urlGnhEp
— Nilesh Trivedi (@nileshtrivedi) June 29, 2023
On average, it costs $41,000 to replace solar panels.
Earlier this year, another hail storm wiped out thousands of acres of solar panels in Texas.
Giant hail is not the only extreme weather event that can damage solar panels and infrastructure. Fires, lightning, extreme winds (and sand and dust deposits from these winds), and heatwaves can reduce power output. If solar panels reach temperatures exceeding 149 °F then they’re likely to start losing efficiency.
Even an increase in cloudiness can cause problems for solar power generation. On a partly cloudy day, production can drop by 10% to 25%, costing solar operators more than $5.25 billion a year.
An increase in global temperature could:
- Decrease equipment efficiency
- Increase operational costs
- Lower the capacity of underground conductors
Solar power is vulnerable to water supply and changes in rainfall caused by heatwaves or droughts. As solar plants are normally located in dry areas, they use wet cooling systems, which need a significant amount of water to run efficiently.
Solar power generation can also be unreliable. This means the storage of solar energy is key to successfully scaling up this energy source globally. The challenge is to correctly balance the supply of solar with the demand for energy from consumers. This requires a deep understanding of historical weather data.
Wind Power
Wind power in the US has more than tripled over the last decade and is now the biggest source of renewable energy in the country. It generates 7.9% of the country’s electricity and more than 20% of the electricity in six states.
You might think that strong winds would benefit the production of wind power, but this is not necessarily the case. The Office of Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy explains,
“Every wind turbine has an anemometer that measures wind speed and a wind vane to keep track of the wind’s direction. When the anemometer registers wind speeds higher than 55 mph (cut-out speed varies by turbine), it triggers the wind turbine to automatically shut off.”

Extreme wind speeds, especially when there are direction changes, gusts, and shears can:
- Drastically increase turbine load
- Threaten the structural integrity of towers and blades
- Cause fatigue and damage to turbine components
- Reduce output
It’s not just hurricanes that threaten wind operations. During Winter Storm Stella in 2017, the five turbines installed at Block Island Wind Farm –– the first US offshore wind farm –– shut down when winds reached more than 55 mph.

More research is being done into creating weather-resilient wind turbines.
At the same time, low winds also mean wind turbines cannot operate correctly.
On the flip side, storms usually have a positive effect on wind power generation, as electricity production rises sharply during high winds.
In the UK, Storm Pia in 2023 provided more than half of its electricity that day.
🆕 Record for the average electrical power output from Great Britian’s wind turbines over a 24 hour period (20.6GW)
🗓️ Previous record from January was 20GW
👉🏾 https://t.co/KgWht7mON7 @ElecInsights @DraxGroup #energy #renewables #StormPia pic.twitter.com/ath2DeUsje— Chris Woods (@chrismwoods) December 21, 2023
In early 2020 during storm Sabine, more than 60% of Germany’s electricity supply was provided by wind energy.
However, when you combine strong winds with waves from extreme weather events, offshore wind farms suffer.
Extreme weather events can damage infrastructure, while hurricanes and storm surges can damage offshore wind farms and affect the lifespan of turbines. Being able to access and maintain wind turbines is also a problem during storms.
Aside from the extreme wind, even small changes in weather parameters put pressure on generation and supply:
- Gradual changes in precipitation, temperature, and near-surface humidity lead to more icing on the turbine blade, reducing power output
- Dust deposits and drier air can also lead to more icing on the turbine blades and reduce power output
- Maintaining and repairing wind farms in permafrost regions is challenging due to the harsh conditions.
- A rise in temperature could increase operational costs and affect the efficiency of the equipment.
- Changes in daily or seasonal distribution of wind affect profitability
Gaining a greater understanding of climate and weather, their potential interruptions, and what wind power resources will be available when can help ensure the smooth running of operations, even with seasonal variability.
If we can more accurately predict output, then we can avoid costly overproduction and coordinate the use of different energy sources better.
Hydropower
The United States is the fourth-largest producer of hydropower in the world, and its relatively low operational costs make it an attractive energy source.
However, hydropower generation around the world varies from year to year according to shifts in weather patterns and other local operating conditions.
Changes in weather patterns can affect the hydrologic cycle (the movement of water over the earth) that underpins hydropower. Hydropower production is dependent on precipitation, which leads to water in rivers and reservoirs. As such, this renewable energy is at the mercy of more extreme weather events, such as droughts and floods, which have been increasing significantly in recent years.
In a severe drought, electricity generation levels can drop as much as 88% while flooding can overwhelm and damage the transformer and electrical equipment within hydro systems. This can cost up to $10,000 to repair.
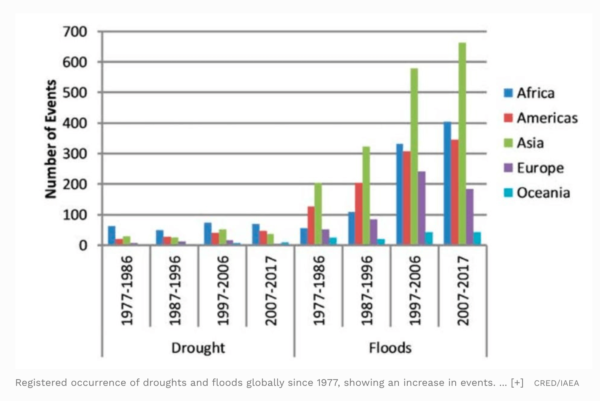
A drought in Indonesia in 2011 reduced generating capacity in two hydroelectric power plants, which led to estimated financial losses of $51.5 million.
The decreasing volume and increasing temperatures of rivers and lakes caused by changing precipitation and warming poses problems when it comes to cooling efficiency and water availability.
In fact, a drought in 2021 greatly reduced water supply leading to California’s hydropower plants’s power generation being 48% below the 10-year average (2011–2020).
In 2022, the famous Hoover Dam had to greatly reduce its water flow and power production due to low water levels.
It’s important to mitigate these weather events as a whole through better forecasting and data use.
Predicting the Future with Weather Intelligence
Moving from fossil fuels to renewable energy makes it even more important for energy producers to get accurate information about historical, current, and future weather.
Often, power producers have been reactionary when it comes to adverse weather conditions and need to respond faster and more proactively.
As the first 12 to 24 hours during and after a weather event are the most important, it’s important to be able to know when the event is coming, where it will hit, predict the damage, and prepare a response. This helps to:
- Mobilize resources ahead of time
- Keep customers informed with timely updates
- Restore power faster
It is key to provide reliable, consistent renewable energy, and sudden drops or surges in supply can destabilize the grid.
After a partial solar eclipse in 2015, German grid operators had to balance out a 2,674-megawatt fall and a 4,111-megawatt rise in solar power within the 15-minute slots that the electricity exchange works on. Using weather forecasts, operators were able to predict the fluctuation of solar power production, prepare for the event, and keep the grid stable.
Being able to predict the future with weather intelligence software that uses long-range and hyper-local forecasts can ensure a reliable supply of energy and stabilize prices.
Anton Orlov, senior researcher at the Center for International Climate and Environmental Research, notes:
“Having information about how hot, cold, humid, dry or windy the upcoming season will be can be critical for estimating how high or low both power demand and renewable power production will be that season.”
Both everyday weather conditions and extreme weather events can have a huge impact on energy production and the bottom line. Whether it’s damage to expensive equipment or lost energy production from a storm, the weather is constantly costing you money.
That’s why your renewable energy business needs weather intelligence to provide accurate and actionable weather data to power your operations.
Gain Actionable Insights with Tomorrow.io
You can’t ignore the risks posed by not understanding and proactively managing weather conditions. That’s why every renewable company should invest in a weather intelligence solution.
Tomorrow.io’s weather intelligence solution provides 24/7 hyperlocal minute-by-minute insights for historical, real-time, and forecasted weather impact. You can see exactly when, where, and how the weather will impact your company.
These forecasts help you become aware of the risk of disruption and damage from storms and flooding at an earlier stage, enabling you to better prepare.
Tomorrow.io’s weather intelligence software can help you:
- Protect valuable assets such as panels and turbines from weather-related risks, and quickly restore damage
- Ensure safe working conditions for employees during maintenance and repair procedures
- Maximize operational efficiency to better adjust to weather-driven supply and demand and improve hydro, solar, and wind output
- Optimize the use of resources to better plan for dips or spikes in production and increase consistent energy production
- Automate operational decision-making and action plans to help you increase efficiency, reduce risk, and decrease unnecessary costs
Stay Ahead of the Weather
As the most commonly used renewable energy sources all depend on the weather, maintaining supply and demand and ensuring a stable grid present unique challenges. Weather intelligence takes the guesswork out of renewable energy production by delivering deep historical data, powerful forecasting, and a dashboard for easy operational decision-making.
FAQ
What is precision weather forecasting for renewable energy?
Precision weather forecasting for renewable energy is the use of advanced weather models, AI, and hyperlocal data to predict weather conditions that directly impact renewable power generation. Unlike general forecasts, precision forecasting focuses on site-specific factors like wind speed, solar radiation, cloud cover, and temperature. This level of accuracy helps wind farms predict turbine output, solar farms anticipate dips in energy production from cloud cover, and grid operators balance supply and demand more efficiently. By knowing exactly when and where weather changes will occur, energy companies can maximize production, reduce downtime, and make better operational decisions.
What is renewable energy weather forecasting software for equipment protection?
Renewable energy weather forecasting software for equipment protection is a specialized tool that uses advanced weather insights to help operators safeguard valuable infrastructure like wind turbines, solar panels, and battery storage systems. Extreme weather such as hail, lightning, high winds, or freezing temperatures poses a serious risk to renewable energy assets. Forecasting software monitors these conditions and provides early warnings, allowing operators to take proactive measures such as shutting down turbines before damaging gusts, adjusting solar panel angles ahead of a hailstorm, or protecting battery systems from temperature extremes. This type of software reduces costly equipment damage, minimizes downtime, and extends the lifespan of renewable energy assets while ensuring continuous power generation for the grid.